Data storage
The on-premises installation was designed to use the local file system for data storage, and the default configuration reflects this. File system based storage is recommended for most installations - it’s fast, and can be used for a single server installation as well as for a multi-server installation where you can share a persistent file system between server nodes.
Alternatively, Amazon Web Services S3 (or an S3 compatible service) and Azure Blob Storage can be used for data storage. Please be aware that, given the additional latency involved, you may encounter performance issues when using these options, and you may wish to enable caching.
Workspace data
Amazon Web Services S3
The basic steps to configure S3 are:
- Create a bucket under your AWS account (folders named
workspacesandreviewswill be created in this bucket). - Create a new programmatic access user in AWS, with the following permissions:
AmazonS3FullAccess. - Modify your
structurizr.propertiesfile to configure AWS S3 integration as follows:
| Property name | Property value |
|---|---|
structurizr.data | aws-s3 |
aws-s3.accessKeyId | Your AWS API key ID. |
aws-s3.secretAccessKey | Your AWS API secret access key. |
aws-s3.region | Your AWS region (e.g. us-east-1). |
aws-s3.bucketName | Your S3 bucket name. |
aws-s3.endpoint | Your custom S3-compatible endpoint. |
aws-s3.pathStyleAccess | Enables path-style access (false by default). |
Alternatively, you can leave the aws-s3.accessKeyId and aws-s3.secretAccessKey parameters unset, and the on-premises installation will use the “Default Credential Provider Chain” to search your environment for the credentials, as described at Working with AWS Credentials - Using the Default Credential Provider Chain.
You will need to enable bucket versioning if you’d like to use the workspace versioning feature.
Azure Blob Storage
- Authentication: access key only
- Workspaces: yes
- Reviews: no
The basic steps to configure Azure Blob Storage are:
- Create a container under your Azure storage account.
- Modify your
structurizr.propertiesfile as follows:
| Property name | Property value |
|---|---|
structurizr.data | azure-blob |
azure-blob.accountName | Your Azure data storage account name (just xxx, not the full URL of https://xxx.blob.core.windows.net). |
azure-blob.accessKey | Your Azure Blob Storage access key. |
azure-blob.containerName | Your Azure Blob Storage container name. |
You will need to enable versioning for blobs if you’d like to use the workspace versioning feature.
Caching
You may encounter performance issues if you have a high number of workspaces, particularly when using the AWS S3 or Azure Blob Storage data storage options. To counter this, you can enable caching of the workspace metadata. If you have a single on-premises installation server, a simple local in-memory cache is sufficient. Add the following to your structurizr.properties file to enable it:
structurizr.cache=local
And if you have multiple on-premises installation servers, you’ll ideally need to use a distributed cache. At this time, only Redis is supported (change the Redis host/port/database/password as required):
structurizr.cache=redis
structurizr.redis.host=localhost
structurizr.redis.port=6379
structurizr.redis.database=0
structurizr.redis.password=
The cache expiry can also be modified if required (the value is minutes, the default is 5):
structurizr.cache.expiry=10
Search indexes
Elasticsearch
The default configuration uses Apache Lucene for search functionality, storing search indexes on the local file system. This is sufficient for a single server installation, but Apache Lucene’s search indexes are not designed for concurrent access from multiple processes. To run the Structurizr on-premises installation across multiple servers, for high availability, you’ll need to use Elasticsearch instead. You can use a local Elasticsearch installation, or a service provided by a cloud provider. Version 6.8.10 and above is recommended.
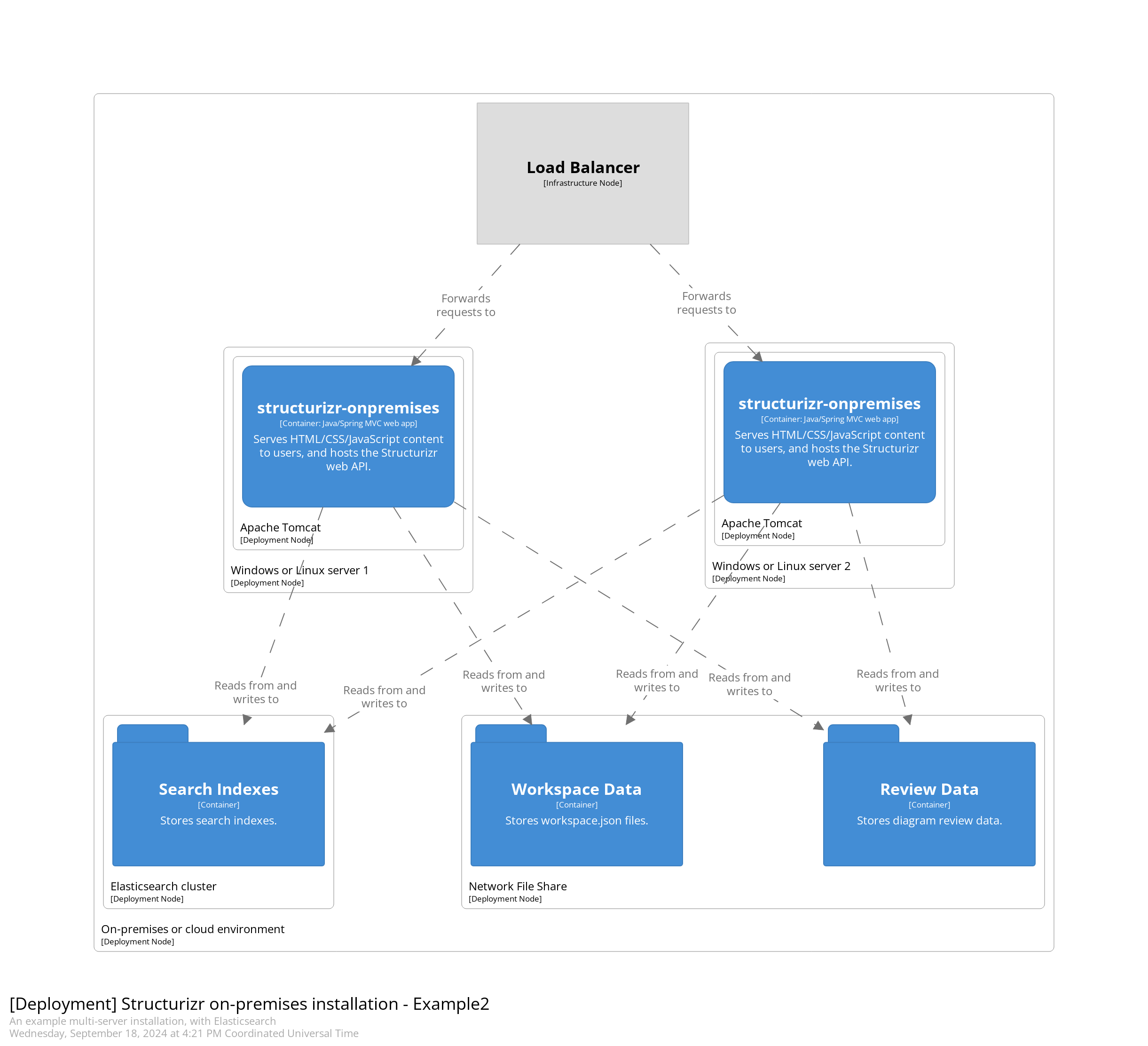
Modify your structurizr.properties file to configure Elasticsearch integration as follows:
| Property name | Property value |
|---|---|
structurizr.search | elasticsearch |
elasticsearch.protocol | The protocol used to communicate with Elasticsearch: http (default) or https. |
elasticsearch.host | Your Elasticsearch hostname/IP address (default: localhost) |
elasticsearch.port | Your Elasticsearch port number (default: 9200). |
elasticsearch.username | The username used to connect to your Elasticsearch instance, if applicable. |
elasticsearch.password | The password used to connect to your Elasticsearch instance, if applicable. |